With growing access to healthcare at home, injectable medicines are increasingly being used outside of hospital settings. Whether it is insulin, antibiotics, or vitamins, patients and caregivers must follow safe practices to avoid complications.
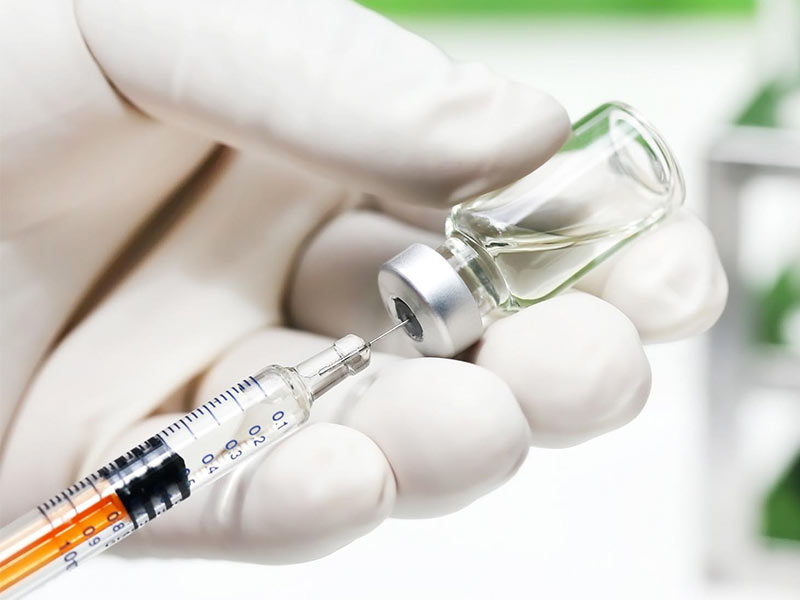
Guidelines for Safe Injection Use at Home
Use Only as Prescribed
Never self-medicate with injectable medicines. These should only be used if prescribed by a registered doctor. Always follow the dosage and instructions given.
Maintain Clean and Sterile Conditions
Before giving an injection:
- Wash your hands thoroughly
- Use new, sterile needles and syringes
- Clean the injection site with alcohol swabs
- Avoid touching the needle
Learn the Correct Technique
Administration technique varies depending on the type of injection—whether it is subcutaneous, intramuscular, or intravenous. Proper training is essential and should be taken from a certified nurse or doctor.
Disposal of Sharps
Used needles and syringes should never be thrown into household garbage. Instead, place them in a puncture-proof sharps container and dispose of them at a medical waste collection point.
Monitor for Side Effects
After giving the injection, observe the patient for any unusual symptoms such as swelling, rash, fever, or difficulty in breathing. In case of any adverse reaction, contact a medical professional immediately.
Storage and Handling
Store injectable medicines at the recommended temperature. Many require refrigeration. Always check the expiry date before use and avoid using medicine that looks cloudy or discolored.
Conclusion:
Home use of injectable medicines can be safe and effective if proper hygiene and medical instructions are followed. Always stay informed, trained, and prepared to ensure safety and success.

Leave a Reply